Shenzhou, Chang’e, Tianwen & Co.: Info Shymkent is presenting detailed information of the big flagship mission of Chinese Spaceflight in the last 20 years.
Chang’e- Chinese Moon missions
The Chinese missions to the moon are called Chang’e. They are named after the Chinese Goddess of the Moon. The Chinese moon program was started in 2003. The huge goal in Chinese Spaceflight to establish a manned moon base on the moon surface. China accomplished all six robotic missions to our cosmic neighbor successful.
- 2007: Chang’e-1 (Moon orbiter)
- 2010: Chang’e-2 (Moon orbiter and later deep space mission)
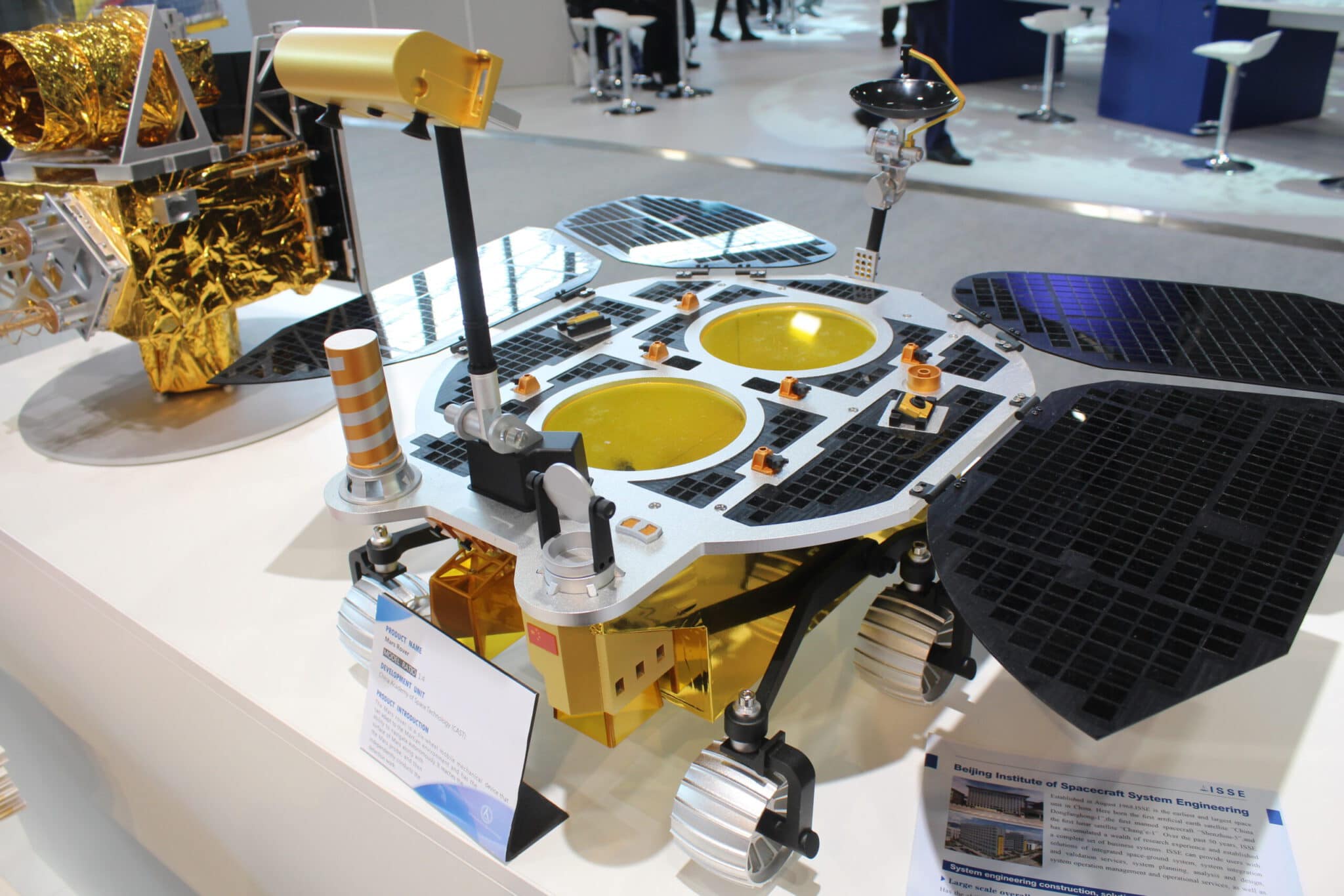
- 2013: Chang’e-3 (with Rover Yutu on the moon)
- 2019: Chang’e-4 (with Rover Yutu-2 at the far side of moon)
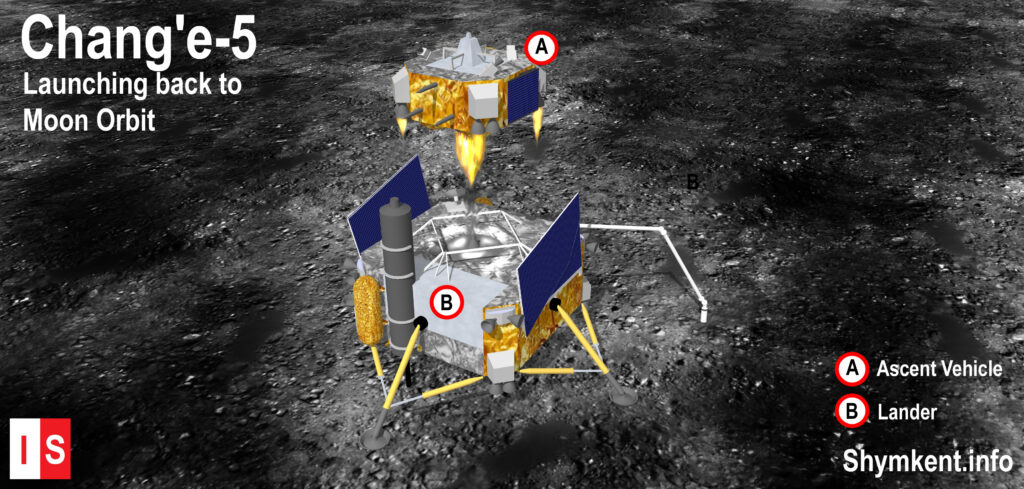
- 2020: Chang’e-5 (Moon sample return mission)
- 2023: Chang’e-6 (Moon sample return mission at a icy moon pole)
- 2024: Chang’e-7 (Moon Orbiter, Relais Satellite, Lander, Rover & Hopper)
- Near future: Yuegong (International Science Moon Station)
Tianwen – Chinese planetary missions
- 2011: Chang’e-2 (L2 Earth-Sun-Point and visit of Asteroid 4179 Toutatis)
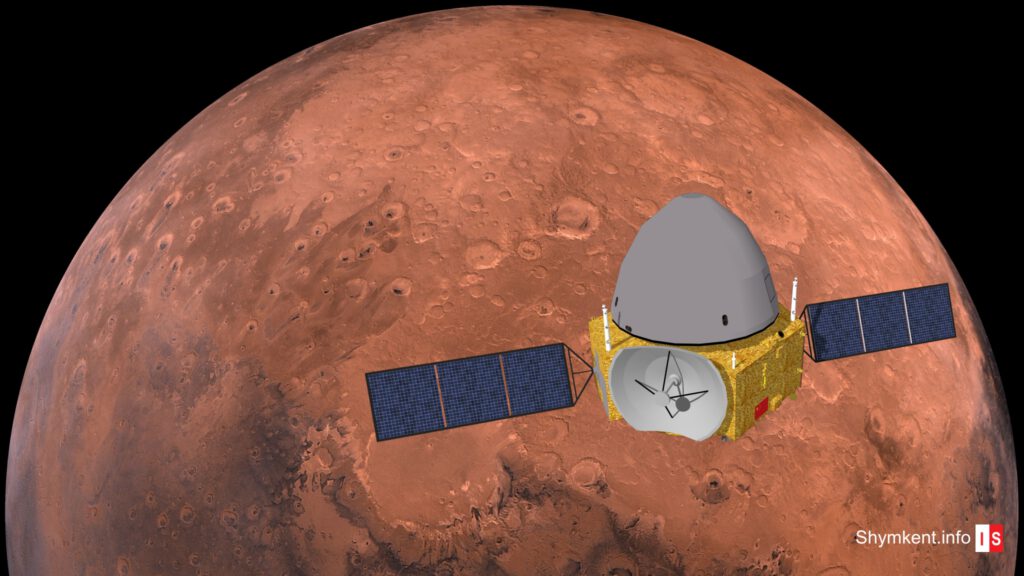
- 2020: Tianwen-1 (Mars Orbiter with Landing vehicle and rover)
- 2026: Planned Asteroid sample-return mission
- 2029: Planned Planetary mission to Jupiter (2029) and Uranus (2049)
Shenzhou – Chinese manned spaceflight
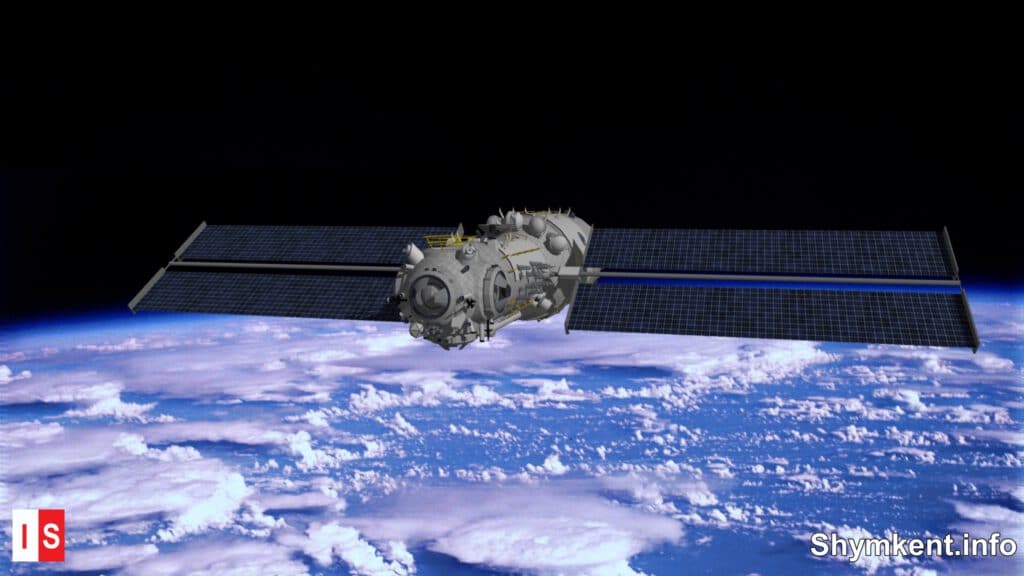

- since 1999: Manned Shenzhou flights (manned spacecraft)
- September 2011: Tiangong-1 (1st space laboratory)
- September 2016: Tiangong-2 (2n space laboratory)
- since 2017: Tianzhou flights (Cargo spacecraft)
- April 2021: Tianhe (Core module of Chinese Space Station Tiangong)
- 24th July 2022: Wentian (1st Science module of Chinese Space Station – Tiangong)
- 31st October 2022: Mengtian (2nd Science module of Chinese Space Station – Tiangong)



